Cross-Check
An eye for an eye is not a good philosophy for life, but it may be true in chess. Learn how cross-checks can turn the tables in chess games to help you win more.
Here is what you need to know about cross-checks:
What Is A Cross-Check In Chess?
A cross-check happens in chess when a player gets out of check and delivers a check to the opponent simultaneously. Cross-checks usually occur when a piece blocks a check and attacks the opponent's king at the same time or reveals a discovered check.
Why Is The Cross-Check Important?
Although rare, cross-checks are important because they can help a player to take the initiative. This feature proves to be crucial in some endgames, such as the relatively common queen and pawn versus queen endgame.
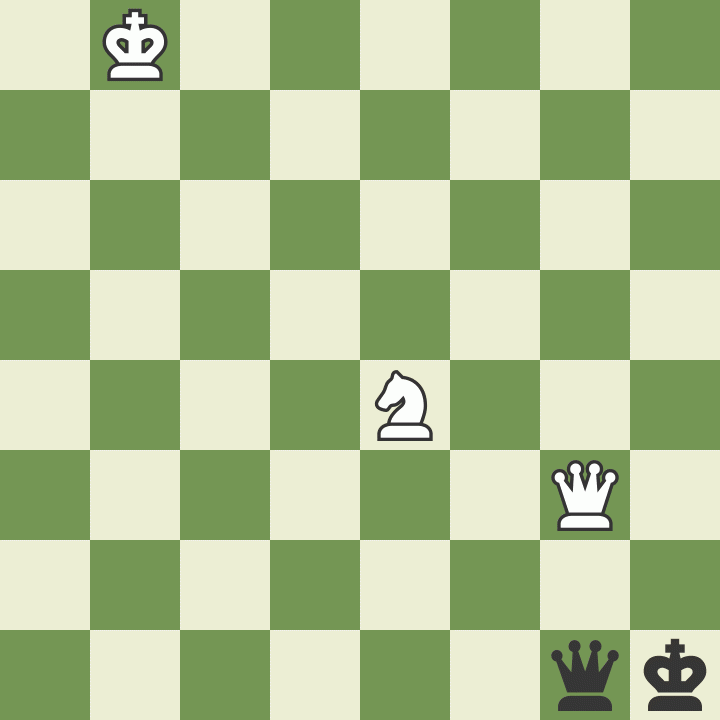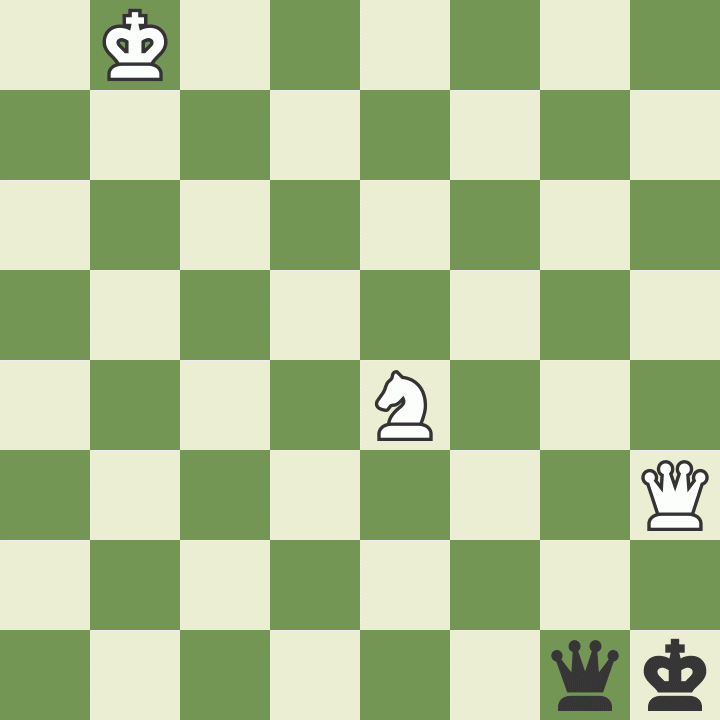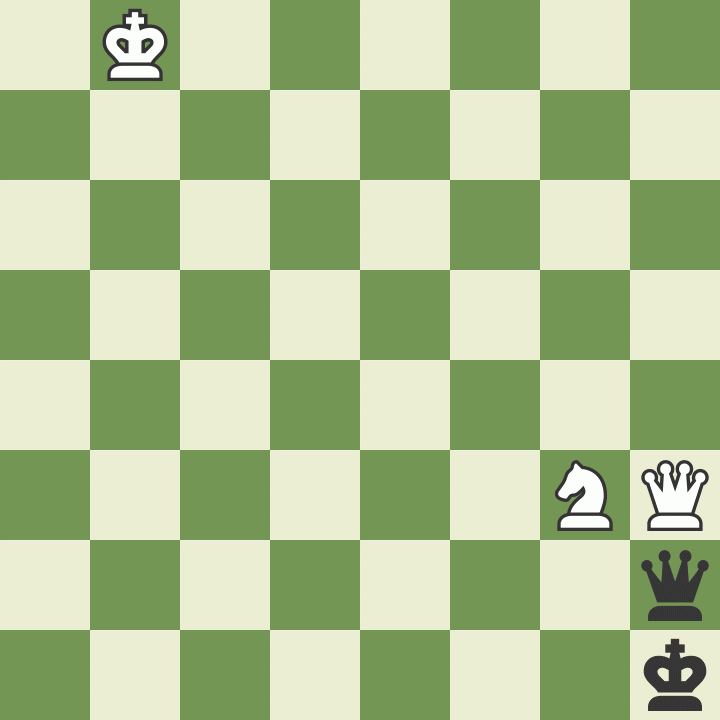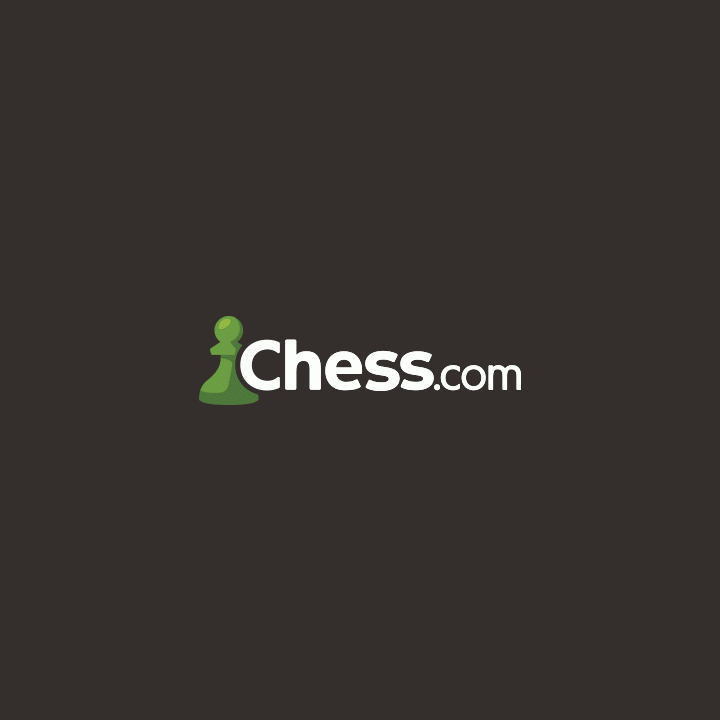
An encounter between GM Mikhail Botvinnik and IM Nikolay Minev in 1954 is an excellent example of how cross-checks can help in this type of endgame. Botvinnik was a pawn up, but Minev would be able to draw the game if he could either take the pawn or force a threefold-repetition.
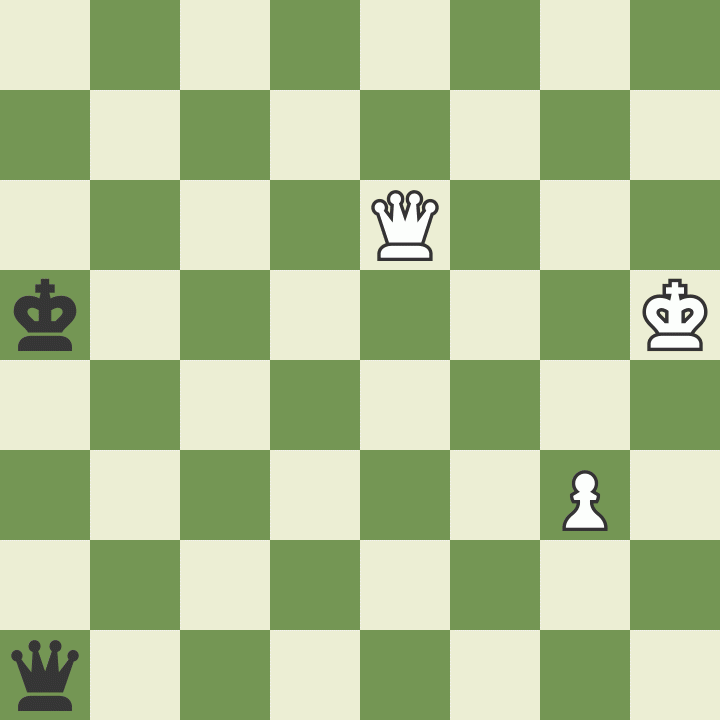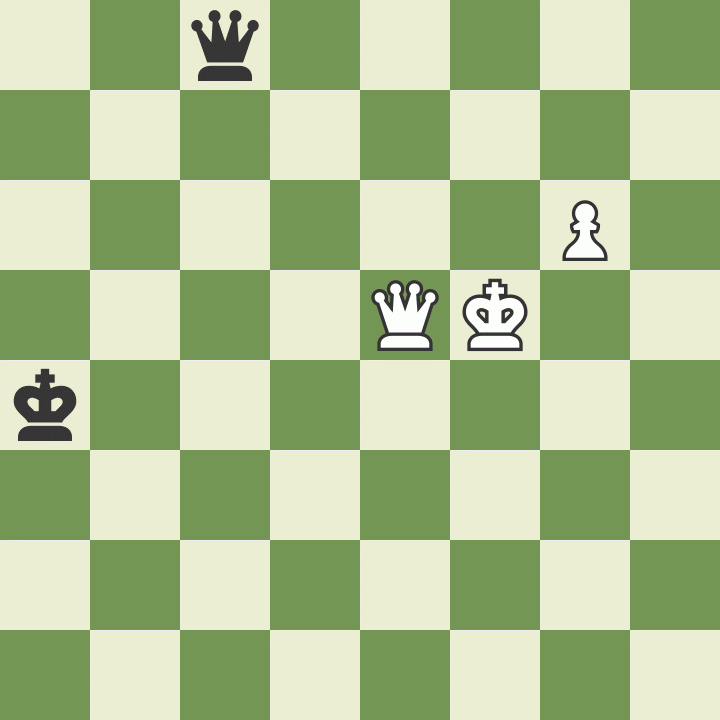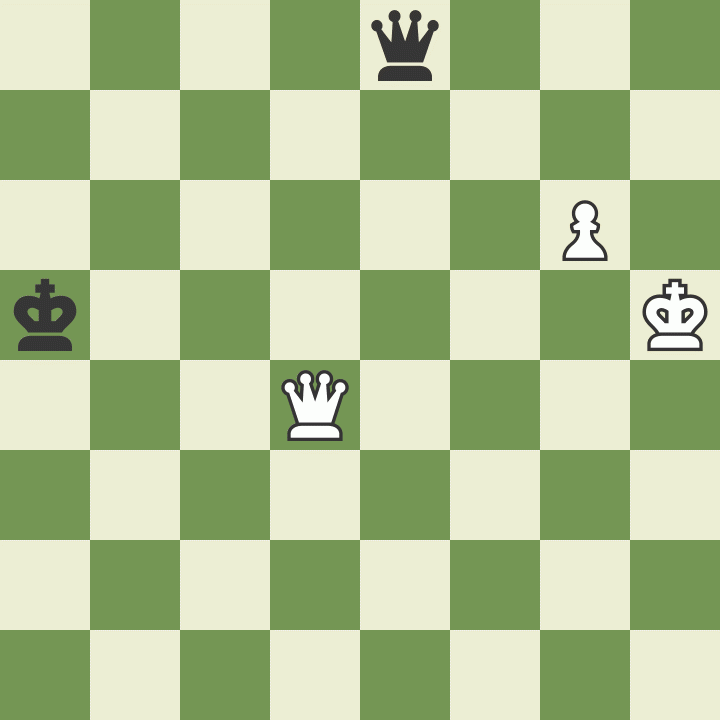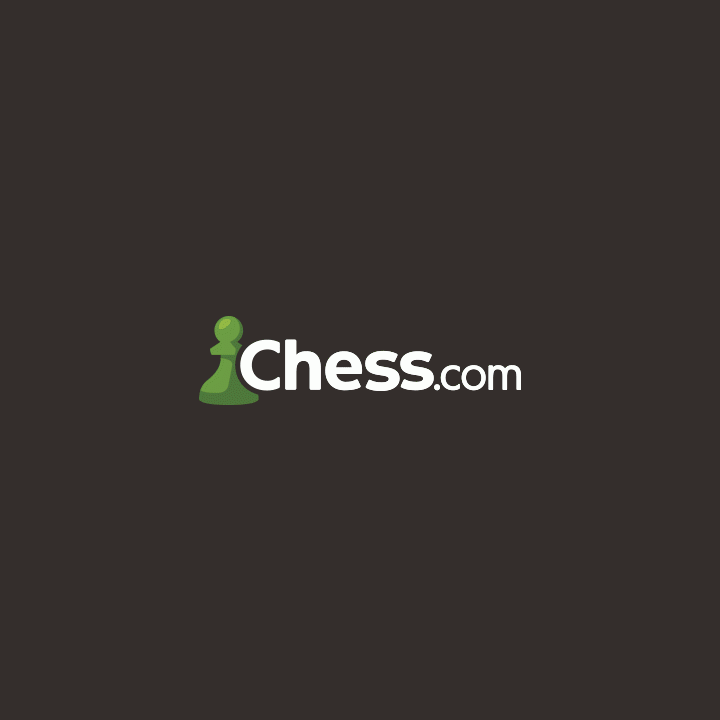
This battle lasted for more than 30 moves until the following position arose. Botvinnik's king was in check, and he had to decide how to get out of it.
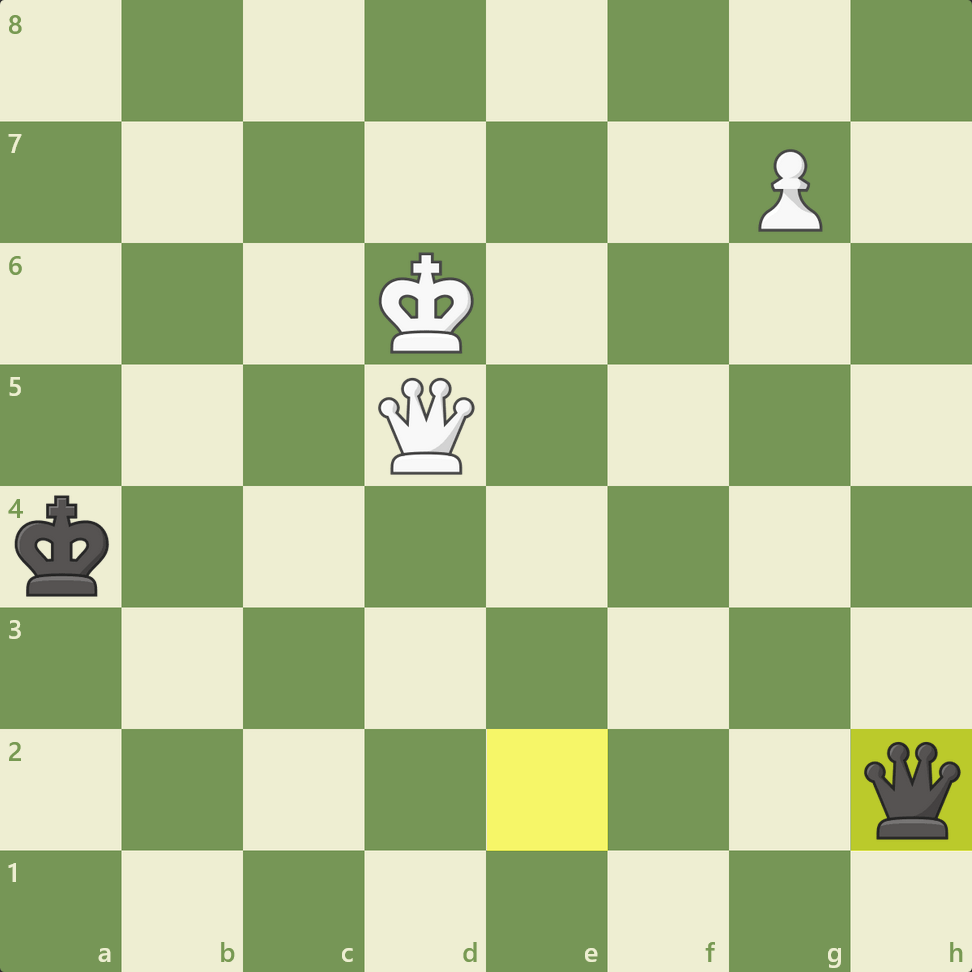
White took this opportunity to make a king move that uses the concept of cross-checking to end the game. Botvinnik played 91.Kc5, and Black resigned since there is no way to keep checking White's king and stop the g7-pawn's promotion.
As you can see from the example above, using cross-checks to gain the initiative can be the difference between winning or not.
Test Your Skills
Now that you know what a cross-check is and how you can use it to your advantage, it's time to test your skills. Solve the puzzles below using cross-checks to gain an edge over your opponent.
Puzzle 1: In this game, GM Lajos Portisch checked GM Jozsef Pinter with his rook. Can you see Pinter's winning continuation?
Puzzle 2: During the 1964-65 USSR Championship, GM David Bronstein was playing Black against Nikolay Bakulin, who played 31.Qf5+ to attack Bronstein's king. Can you see Black's two moves that created an unstoppable threat and forced White to resign?
Puzzle 3: In this game between GM Vladimir Akopian and GM Sergey Karjakin, Black is threatening to take the b2-pawn to draw the game with a perpetual check. Can you see Akopian's brilliant move that sets up a cross-check that stops Karjakin's idea and threatens mate in one? Hint: Look for an underpromotion!
Conclusion
You now know what a cross-check is and why it's important. Head over to our Lessons page to learn other ways to develop the initiative and win more chess games.